How To Treat Excessive Hair Shedding Effectively?
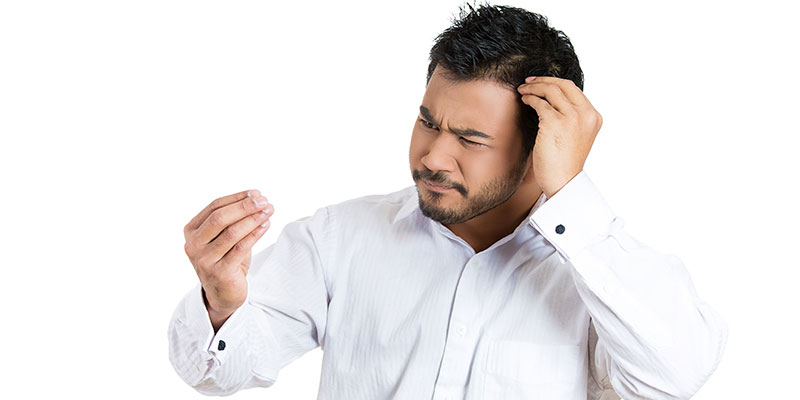
A healthy head of hair will shed around 100-150 strands on a daily basis. If you notice that you are shedding more than the normal amount of hair, it is referred to as telogen effluvium or excessive hair shedding, which, if untreated, can lead to hair loss.
In This Article

What Is Hair Shedding?
Hair-shedding is a normal part of a natural hair growth cycle. The growth cycle begins with the anagen phase which is the growing phase of the hair follicle. This stage lasts for about 3-5 years. Next comes the catagen phase which is the intermediate phase where the hair follicle’s structure starts collapsing. This phase lasts for between 1-2 weeks. The final phase is the telogen phase which is when your hair sheds or falls, to make room for new hair. This phase lasts for 3-4 months and only about 10% of our hair will be in the telogen phase at any given point time.
Watch this video now
The Difference Between Hair Loss And Hair Shedding
Hair loss and hair shedding are two different conditions. They might look the same but the underlying reasons behind these two hair conditions are completely different.
Hair shedding is a natural and normal process. However, when there is excessive hair shedding, it is categorized as hair loss, which is an abnormal condition. Hair loss occurs when an internal or external factor such as heredity, harsh hair care products, medication, etc., hinders its growth. It is also known as anagen effluvium. Major reasons causing hair loss are heredity, medication, hormonal changes, medical conditions, etc.
Hair shedding usually occurs as a result of some stressful event such as losing weight, pregnancy, recovering from an illness, etc. Unlike hair loss, excessive hair shedding usually stops when its trigger factor disappears.
The terms hair shedding and hair loss are often used interchangeably, but diagnostically, they mean different things. In many cases, excessive hair shedding is a temporary condition. At times, treatments are required.
The easiest way to determine whether you are experiencing hair shedding or hair loss is to give it time. If you notice that hair has stopped growing at certain places for 2-3 months or more, then it is likely a case of hair loss. Hair loss requires medical treatment and it is best to visit your dermatologist for a comprehensive consultation.
Must Read: Hair Loss Treatment That Work
What Causes Excessive Hair Shedding?
A number of factors affect the hair growth cycle, causing the hair to shed excessively. Depending on the causes, hair shedding may be reversible. They are:
- Stress – Stress and anxiety can trigger and accelerate hair shedding. By affecting various physiological functions of the body, stress can result in a lack of sleep or appetite. Our body reacts to stress by prematurely speeding up the resting phase of the hair growth cycle. This results in excessive hair shedding.
- Lack of Vitamins – If your diet lacks vitamins and minerals that nourish the hair, then it may also trigger hair shedding. A diet rich in calcium, protein, iron, vitamin D, biotin etc. can help prevent hair shedding. Taking the right vitamins for shedding hair can help you overcome the problem.
- Pregnancy – Pregnancy causes the body to go through multiple changes which result in a hormonal imbalance and this in turn influences the hair growth cycle resulting in hair shedding.
- Illness – Certain illnesses may trigger a hormonal imbalance in the body, leading to excessive hair shedding.
- Weight Loss – During a weight loss period, the body goes through major physiological changes. In certain cases, it can lead to an intense period of hair shedding.
- Post-Pregnancy – It is common for new mothers to experience excessive hair shedding two months after they have given birth. This phase usually lasts for about four months and is just a temporary phase.
- Birth Control Pills – When women stop taking birth control pills, they can experience excessive hair shedding.
Also Read: What Causes Of Hair Loss In Men And Women?
Seasonal Hair Fall – Myth or Reality?
Many people tend to notice hair shedding in the late fall and winter. During this period, hair shedding in men and women tends to increase. According to medical research, our scalp responds to changes in daylight hours. The longer daylight hours in summers triggers the telogen phase and therefore hair shedding occurs in late autumn or winter. The process is completely normal and can be prevented by taking the vitamins essential for healthy hair growth.
Does Hair Grow Back On Its Own?
In most cases, shed hair usually grows back. It depends on the stage of the hair growth cycle during which it occurs and the cause behind hair shedding. If hair shedding is within the normal range, it is temporary and the hair will re-grow over several months. In extreme cases, hair might not grow back until preventive measures are taken to stop the hair from shedding.
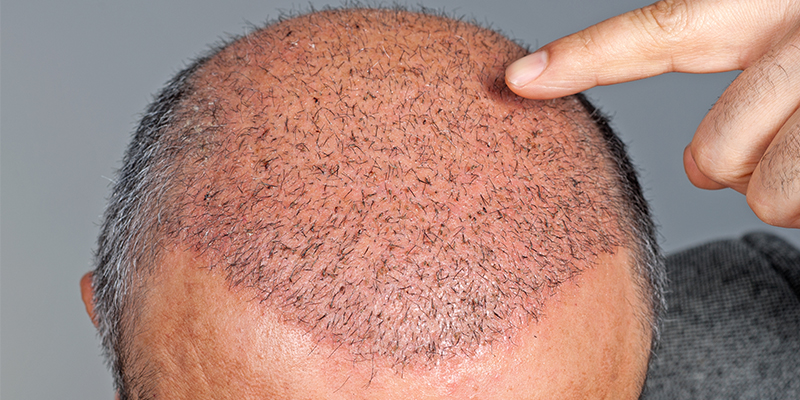
Excessive Hair Shedding Treatment
Usually, excessive shedding is a temporary condition but there are certain cases where you will need to consult a dermatologist. In cases where excessive hair shedding is genetic or results in balding, a few treatments can help.
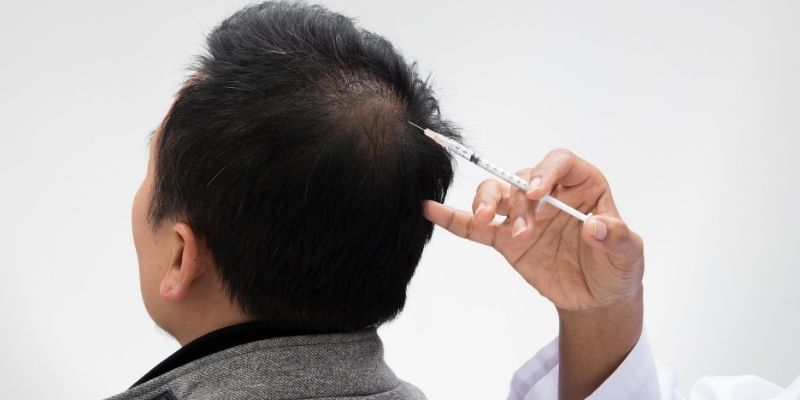
- Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy – PRP Therapy is a non-surgical treatment which uses the patient’s platelets to restore lost hair and stimulate hair follicles to grow hair. The platelets are infused with growth factors and injected directly onto the scalp. This treatment is extremely effective in the regeneration of lost hair.
- Minoxidil – Minoxidil is a topical solution which can be applied directly on the scalp. It can be used by both men and women. It treats hair shedding by prolonging the hair’s growth phase and preventing some of the hair from entering the telogen phase. Minoxidil can also help in the thickening of hair strands.
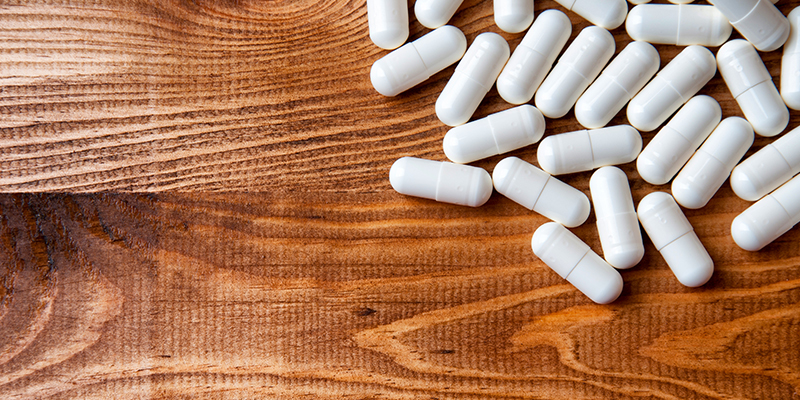
- Finasteride – Approved by the US-FDA, finasteride is available in pill form by prescription only. Like Minoxidil, it promotes hair growth at the same time as it puts a stop to shedding. However, it is only suitable for men.
Also Read: How Much Does PRP Treatment Cost?
Tips To Stop Excessive Hair Shedding
Here are some tips you can use to volumize your hair
- Maintain strict scalp hygiene. Depending on how oily or dry your scalp is, only wash as frequently as required.
- Consult a dermatologist who can help you choose the right shampoo and conditioner based on the quality of your scalp.
- Do not tie your hair immediately after washing your hair as the hair breaks easily when wet. Avoid high-tension hairstyles as it can lead to traction and irreversible hair loss.
- Avoid hair breakage. Use a wide-toothed comb to detangle curly hair.
- Do not go on quick weight loss diets or crash diets as they can also trigger hair shedding.
- Avoid colouring or straightening your hair frequently. If you must, make sure you keep a gap of 2-3 months between each treatment.
- Air dry your hair after a bath. Excessive blow drying, especially with hot air, can damage hair quality. If it is unavoidable, use your hair dryer on cool mode.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is normal to shed between 50 and 100 hairs a day as part of the natural hair growth cycle. This is a normal process where old hairs are replaced by new ones. Excessive hair shedding, medically known as telogen effluvium, occurs when a person sheds significantly more than this on a daily basis.
Yes, stress is a very common cause of hair shedding. Significant physical or emotional stress can push a large number of hair follicles into a “resting” or shedding phase prematurely. You might not notice this immediately; the excessive shedding often becomes apparent a few months after the stressful event has occurred.
A balanced diet rich in certain nutrients is essential for healthy hair. Key nutrients for hair health include protein, iron, zinc, and vitamins like C, A, and E.
- Protein: Since hair follicles are primarily made of protein, ensuring you get enough from sources like eggs, lean meat, and legumes is vital.
- Iron: An iron deficiency can be a major cause of hair loss. Incorporating iron-rich foods like spinach and red meat can help.
- Vitamins: Foods like berries (rich in Vitamin C) and nuts (rich in Vitamin E) provide antioxidants that protect hair follicles.
While normal shedding is a natural part of life, you should see a dermatologist or healthcare provider if you notice:
- Sudden and rapid hair loss: A significant, abrupt increase in the amount of hair you’re shedding.
- Patchy hair loss or bald spots: The appearance of distinct, circular or irregular bald patches on your scalp.
- Receding hairline or thinning at the crown: A gradual receding hairline in men or a widening part in women.
- Scalp changes: Hair loss accompanied by symptoms like redness, itching, pain, or scaling on the scalp.
- Lack of regrowth: If your hair doesn’t seem to be growing back after a few months, especially following a known trigger
Yes, in most cases of excessive shedding (telogen effluvium) caused by a temporary event, the hair will grow back on its own once the underlying issue is resolved. For example, hair shedding after childbirth, a severe illness, or a period of intense stress is typically temporary. Normal hair fullness usually returns within six to nine months as the body readjusts and the hair growth cycle returns to normal. However, if the cause is long-term (like chronic stress or a nutritional deficiency that isn’t addressed), the shedding can continue until the cause is managed.