Best Treatment to Get Rid Of Xanthomas
Yellow coloured nodules or patches are often seen around the eyes, elbows, knees, face, and neck, and can indicate a serious underlying health condition that has impacted the metabolism of fat in the body. Xanthomas or xanthomatosis is a term used to describe such patches or deposits. Instant treatment is necessary under the supervision of a doctor and a dermatologist to stop the skin concern from going beyond control.
What Is Xanthoma?
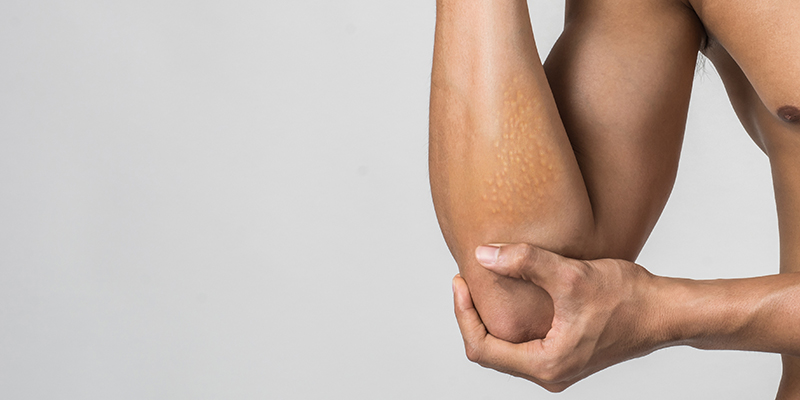
When fatty deposits accumulate in the body and develop into firm nodules under the skin that are yellowish in colour, the condition is termed as Xanthomatosis. The deposits are called as xanthomas or xanthomata. It is a harmless tissue that grows beyond the normal levels and causes the formation of nodules.
Xanthoma histology indicates that the deposits are made up of histiocytes that contain high levels of lipid material in their cytoplasm. They appear yellowish or even orange on the skin’s surface with the size of the nodule varying widely. Usually, no pain is associated and these deposits are often found in clusters under the skin.
Body Areas Affected By Xanthoma
- Feet
- Hands
- Joints (knees and elbows)
- Buttocks
- It is rare but xanthoma on the face is also possible.
Types Of Xanthomas
The classification for the types of xanthomas is based on the location it develops at and also how it develops. Here are the various types –
- Xanthelasma Palpebrum – Commonly known as xanthomas on eye or xanthomas under eye, the flat papules or deposits develop on the upper and lower eyelids in this type
- Tendinous Xanthoma – These are fat lesions associated with tendons or ligaments and are commonly found on the heels, Achille’s tendon, and feet
- Tuberous Xanthomas – Increased cholesterol levels in the body can lead to firm nodules of xanthomas to develop on the skin’s surface at areas of the body that withstand pressure regularly such as the knees, buttocks, elbows, etc. These are painless nodules and can also be multilobulated
- Eruptive Xanthomata – Also called as tuberoeruptive xanthomas, the deposits or plaques are seen commonly on arms, legs, and buttocks. They are very rarely seen on the face. Itchy, red lesions form on the skin due to increased triglyceride levels in the blood. Eruptive xanthomatosis is also associated to diabetes
- Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis – The fat deposits are found in the tendons and the brain in this type of xanthomatosis. Neurological problems often develop leading to seizures, impaired speech, and other serious complications related to the nervous system
- Xanthoma Disseminatum – The lesions appear in large numbers and form reddish brown or yellowish brown bumps on the skin. This particular type of xanthomata spreads easily and can cover large areas like the face and trunk
- Plane Xanthoma – Flat lesions develop anywhere on the body in this type. It is closely associated to high lipid and triglyceride levels in the body
- Diffuse Plane Xanthomas – It is often associated with a blood malignancy and presents flat, yellowish patches in skin folds, on face, neck, and buttocks
- Verruciform Xanthoma – The histology of this type of xanthoma or xanthelasma indicates presence of histiocytes in the epithelial layer of the oral mucosa and other areas of the body.
Also Read: How To Get Flawless Skin?
What Causes Xanthomas?
These fat deposits are caused to increased fat levels in the body, which can be caused by underlying diseases or conditions like –
- Diabetes
- Fat disorder or hyperlipidemia
- High cholesterol (cholesterol xanthoma)
- Hypothyroidism
- Liver conditions that impair bile flow (such as choletasis and primary biliary cirrhosis)
- Hematologic diseases that impacts digestion of fats
- Cancer
- Certain medications like cyclosporine and prednisone
- Genetic predisposition
Also Read: What Is Melasma?
How To Get Rid Of Xanthomas?
To get rid of xanthomata deposits from under the skin, the underlying disease has to be treated. Appropriate medications and therapies used to lower fat levels in the body caused by the underlying disease, can reduce the number of xanthomas. The fat deposits will dissolve by themselves with progressive treatment and the skin’s appearance in the affected region will return to normal. Along with the suitable treatment, changes are necessary in the diet and lifestyle with healthier foods being included in the diet and increased physical activity.
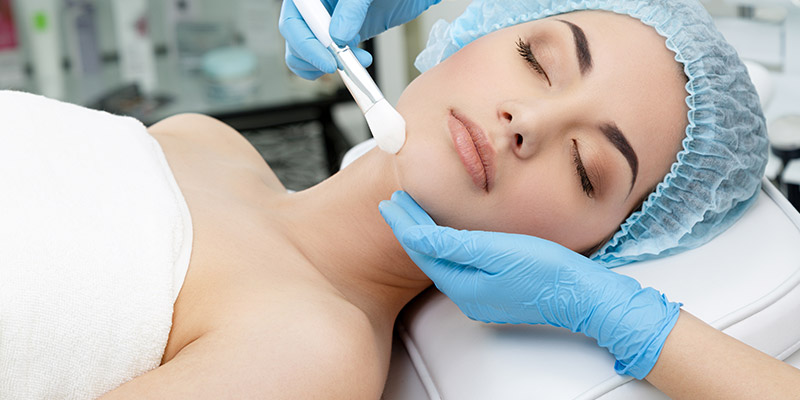
Treatment For Xanthoma
When treatment for xanthomas is considered, the primary motive is to reduce the appearance of the fat deposits on the skin and make the skin’s appearance smoother. These topical treatments are for cosmetic purposes only. They do not target the underlying disease, hence to remove xanthomas for good, the cosmetic treatments mentioned below need to be combined with suitable medical treatments for the underlying disease –
Trichloroacetic Acid
Removal of xanthomas on eyelids is often carried out using topical trichloroacetic acid. The acid is used in varying concentrations (up to 70%) depending on the extent of the plaques on the eyelids. Thorough exfoliation is achieved to get rid of xanthomas palpebrum from the skin around the eyes and reveal healthy, fresh skin present below. The skin around the eyes is sensitive and this treatment should not be carried out at home. Only an experienced dermatologist should perform the treatment to avoid any side effect or irreparable damage to the skin
Laser Therapy
This is a safer method when compared to electrodessication as the intensity of the laser energy can be controlled by adjusting the wavelength or the type of laser being used. The laser light is used for skin ablation which is basically removing the top layers of the skin that are affected. Once the skin heals, the area that is treated has renewed skin instead of the yellowish plaques. Eruptive xanthoma treatment is often performed using this method. The risk of scarring and other side effects like hypopigmentation are minimized when the treatment is performed using US FDA approved equipment and by trained dermatologists.
Also Read: Xanthelasma Treatment
Radio frequency
Studies have shown low voltage radio frequency treatment is effective in case of xanthomas near the eyes or eyelids. It helps in remodeling the skin by stimulating newer collagen and elastin production as heat from RF stimulates cells in connective tissues. It is safe on human eyelids and studies have suggested it as one of the most effective treatment
Cryosurgery
Using liquid nitrogen, very cold temperature is used to remove the xanthomata outgrowths on the skin. Due to extremely low temperature they get removed from the skin.
Electrodessication
An electric needle is used to scrape away the plaques and papules from the skin’s surface formed due to different types of xanthomata such as Achille’s tendon xanthoma or xanthoma tuberosum. This treatment poses the risk of scarring after the treatment is performed
Surgery
When the xanthomata cannot be treated using the above methods, such as in the case of nodules forming on the skin, surgery or excision of the lesions may be required to remove the affected skin. Scarring is very common with this treatment and there is also the chance of an infection developing if the excision is not performed under sterile conditions.
Disclaimer:
This article provides medical information about various procedures for awareness purposes only. We want to help you know about the various treatment options beyond the services available at Oliva Skin & Hair Clinic. We request you weigh the pros and cons of these aesthetic practices and make an informed decision about your skin and hair health.
Also Read: Common Skin Diseases And Treatments
Xanthalesma is a skin condition that should not be ignored and should be treated as soon as possible. Identifying the underlying disease or disorder causing the fat deposits to form is vital for appropriate treatment course to be initiated. Take advantage of cosmetic treatments available to remove xanthomas and use them while you are undergoing the treatment for the causal disease.
FAQs
-
-
Who Is At Risk For Developing Tuberoeruptive Xanthomas?
-
People with high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, and low levels of HDL in the body are at a higher risk of developing tuberoeruptive xanthomas. Rare conditions like cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, homozygous hypercholesterolemia, and b-sitosterolemia also increases chances of developing this type of xanthomas.
-
What Is Xanthoma on the Eyelids?
Xanthomas eye is a common term used for xanthomas palpebrum. Yellowish lesions form on the upper and lower eyelids in this skin condition.
-
What Does Xanthelasma Look Like?
The fat deposits are yellowish in appearance on the skin and can be in the form of lesions or plaques in most types of xanthelasma. Nodules are seen in the xanthomas tuberosum type.