Different Types Of Hair Loss And Available Treatments
What Is Alopecia?
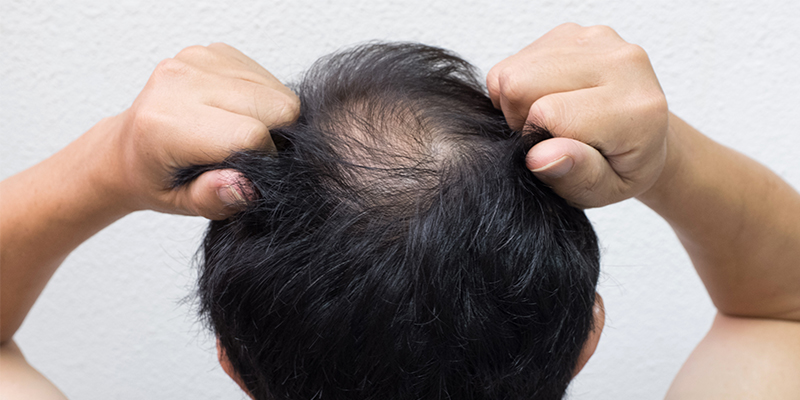
Alopecia refers to a gradual loss of hair, partial or complete, occurring anywhere on the head or on the body. Usually, alopecia, if caused genetically, leads to total baldness in the long run.
There are different factors responsible for hair loss, and each leads to a different type of alopecia. Both men and women of any age can suffer from alopecia anywhere on the body; however, most cases are referred to the scalp. Most people tend to witness noticeable hair loss after the age of 60.
Effective treatment of alopecia requires a proper understanding of its type, as well as its underlying causes.
What Are The Main Causes Of Alopecia?
Primary causes of alopecia in women include:
- Lack of vital nutrients (vitamins and minerals) in the body
- Hormonal imbalances experienced during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, and others
- Stress and tension
- Physical or mental trauma, including fever
- Side effects of medicines, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs and birth control pills
- Drastic changes in the physical environment
- Dehydration
- Faulty hair care techniques
- Medical conditions of the scalp such as psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis
- Any short-term or chronic illnesses
Primary causes of Alopecia in men include –
- Genetics
- Auto-immune related issues
- Scalp-affecting infections and medical conditions such as psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis
- High levels of DHT (dihydrotestosterone)
- Side effects of medicines or surgery e.g. chemotherapy
- Medical illnesses such as high blood pressure, diabetes etc.
Types Of Alopecia And Available Treatments
- Telogen Effluvium – This is an uncommon, but easily treated form of alopecia. Here, more than a healthy number of hair follicles enter the telogen (resting) phase, resulting in temporary hair loss. This kind of alopecia is triggered by trauma, physical strain, or mental stress. Once the causes are no longer present, hair starts to grow back.
Available Treatment – In most cases, exercising often, staying hydrated, and making simple improvements to lifestyle and environment can help. Adequate nutritional supplements can also make a difference. - Androgenetic Alopecia – Androgenetic alopecia is a common form of hair loss occurring in both men and women. In men, it is characterized by a loss of hair starting at both the temples and at the crown, according to the male-pattern of baldness. Women with Androgenetic alopecia experience hair-thinning throughout the parting area.
Androgenetic alopecia results from DHT overactivity in the hair follicles of the scalp. It is genetically inherited, and caused by multiple factors. When it occurs in women, the role of DHT is less clear. Androgenetic alopecia in women is associated with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
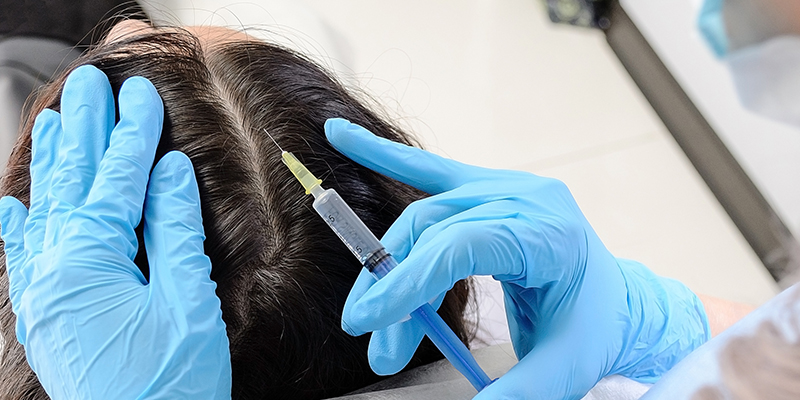
Available Treatment – Oral and topical medications, platelet-rich plasma treatment, hair transplants, and scalp reduction have been used with successful results.
Must Read: What Is Would be Cost of PRP Hair Treatment?
- Alopecia Areata – Alopecia areata is one of the most common types of alopecia occurring in both men and women. It is mainly caused by an autoimmune phenomenon that results in sudden, drastic hair loss on particular areas of the scalp, and noticeable bald patches. The treatment includes supplements, topical solutions, and injections into the bald patches.
Subtypes of Alopecia Areata:
- Alopecia Totalis – Alopecia totalis is an advanced form of Alopecia areata. With this condition, an individual ends up losing hair all over the scalp. It can be triggered by hormonal changes or environmental stress factors. It is recommended to diagnose Alopecia totalis at an early stage. The condition gets harder to treat as it progresses.
Available Treatment – Alopecia Areata and Alopecia Totalis are tough to treat with a single type of therapy alone. A combination of approaches works best. Effective treatments include topically applied or injected corticosteroids, Psoralen and Ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy, narrow-band Ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy, topically applied minoxidil and others. - Alopecia Barbae – Commonly found in men, Alopecia Barbae is often called alopecia of the beard. In this, bald patches form in the beard region. Eventually, this can lead to total loss of beard and facial hair.
Available Treatment – Alopecia Barbae is treated with topically applied or injected corticosteroids. For best results, consult a dermatologist. - Alopecia Universalis – Alopecia Universalis is the most advanced form of alopecia, which leads to complete hair loss across the body. Patients lose hair on the scalp, beard, eyelashes, pubic hair, and other body parts. While the exact reason for Alopecia universalis is unclear, it is often linked to genetics and the autoimmune system.
Available Treatment – Sadly, there is no ideal treatment for Alopecia universalis. Doctors can prescribe auto-immune medicines to help. Though, once the alopecia disease has stopped progressing on its own, a dermatologist can try a hair regrowth plan. - Involutional Alopecia – Involutional alopecia is a form of hair loss that occurs because of the natural ageing process. The main cause behind this type of alopecia is the shortening of the anagen (growth) phase of the hair growth cycle. In this case, hair does not grow as fast as it is shed.
Available Treatment: Involutional alopecia is treated with oral medications, advanced PRP treatment, and advanced laser therapy in combination with topical medications. - Scarring Alopecia – Also known as Cicatricial Alopecia, Scarring Alopecia is a rare condition caused when inflammation or scarring hamper the scalp’s natural ability to grow hair. There are Two Classifications of Cicatricial Alopecia: the primary and the secondary forms.
In primary Cicatricial Alopecia, hair follicles are unable to regenerate hair because of internal issues. In secondary Cicatricial Alopecia, hair follicles are impacted by an indirect cause, such as thermal burns, metastatic cancer, trauma or radiation. In both cases, the hair follicles are replaced by scar tissues and lose their ability to grow new hair.
Available Treatment – Treatment strategies for both primary and secondary Cicatricial Alopecia vary with a single goal: to inhibit the inflammatory process destroying hair follicles. Topical medications such as corticosteroids, oral antibiotics and isotretinoin, can be effective when used along with more advanced treatments such as hair transplantation and scalp reduction. - Traction Alopecia – This type of alopecia happens when hair follicles are damaged from excessive and regular hair-pulling. Tight ponytails, buns, braids, and excessive styling can cause this problem. Traction Alopecia usually takes a while to progress, but can easily be identified at an early stage.
Available Treatments – Traction Alopecia can be treated by styling your hair gently, removing harsh chemical products from our hair care regimen, and nourishing the scalp appropriately. - Anagen Effluvium – Anagen effluvium is a type of non-scarring alopecia, which is also referred to as chemotherapy-induced alopecia. This type of alopecia develops within 2 to 4 weeks of chemotherapy as the hair suffers from a toxic or inflammatory insult. This alopecia leads to fracture of the hair shaft.
- Trichotillomania – Trichotillomania or TTM is a type of alopecia known to be caused by the repeated pulling of one’s own hair. This type of alopecia is associated with an impulse control disorder. Individuals who suffer from TTM fail to resist urges to pull out their own hair and thus face hair loss.
No matter which type of alopecia your hair loss closely resembles, it is best to seek professional help immediately. The dermatologist will have the right tools to diagnose you correctly and suggest the most suitable treatment option available.