Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) – Causes, Treatment And Prevention
The cases of atopic dermatitis are on the rise in India, making it essential to bring about more awareness regarding this skin condition and also different ways to treat it. It may seem like an unmanageable issue, but under the guidance of an experienced dermatologist, you can get relief from your atopic dermatitis symptoms. Keep reading to know what this skin condition is, what are reasons behind it, how does it present itself on the skin, and how you can treat it as well.
What Is Atopic Dermatitis?
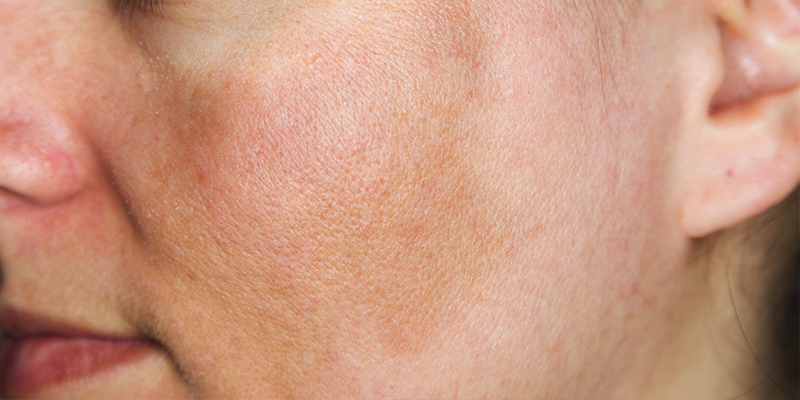
An inflammation of the skin that leads to the formation of dry, itchy skin is called Atopic Dermatitis. It runs in families, which means that it is a hereditary skin disease. The word ‘atopy’ means hereditary, and ‘dermatitis’ is a term used for skin inflammation.
Atopic dermatitis can affect children and adults alike, with many cases being reported in infants too. It falls under the “Eczema” category among skin diseases.
Also Read: What Causes Dry Skin & How To Get Rid Of It?
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis cause is ambiguous, but it is believed to be related to a gene mutation. This mutation weakens the skin barrier causing moisture to escape from the skin very easily and inflammation to occur. An undermined barrier also makes the skin prone to infection, which often occurs in patients with atopic dermatitis.
If the parent has atopic dermatitis, asthma, hay fever or a family history of allergies, the child has higher chances of developing atopic dermatitis. Apart from this, there are certain factors that can trigger an atopic dermatitis flare-up. These include –
- Low humidity levels in the atmosphere
- Cold weather
- Exposure to harsh detergents and soaps
- Seasonal allergies such as pollen
- Allergens such as dust mites
- Allergens in food such as peanuts, eggs, soy, etc.
- Stress
- Sudden changes in temperature
- Cold or flu
- Skin infection
- Certain fragrances or dyes
It is important to note that atopic dermatitis is not contagious, that is, it does not spread from one person to another.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis?
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis are as follows –
- Dry, itchy skin
- Redness in the affected area
- Rash on the affected area such as the face or arm
- Open sores that can be crusted or ooze out a liquid
- Infection leading to small, pus-filled bumps
- Ear discharge
It is a chronic skin condition with its symptoms becoming better or worse every now and then. It usually affects areas like underarms, face, neck, folds of the arms, behind the knees, etc. Atopic dermatitis can also affect the eyes and cause cataract.
Also Read: How To Get Rid Of Small Bumps On Face?
What Are The Stages Of Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis begins most commonly during the infant age. Usually, a rash forms on the cheek or chin. Papules form that become scaly and hard when scratched. These rashes start to develop in other body areas such as the elbows and knees with increasing age of the infant. In many cases, the symptoms die down in a couple of years, but such children are extremely prone to developing an atopic dermatitis flare-up during adulthood.
When this skin condition exhibits itself for the first time during adulthood, the rashes can be located in one area or be widespread.
What Is The Difference Between Eczema And Atopic Dermatitis?
The term ‘eczema’ is used to describe skin inflammations in general. Depending on the cause and the presentation of the skin condition, it is further categorized into different types such as contact eczema, seborrheic eczema, nummular eczema, etc. Atopic dermatitis is a type of eczema and is considered to be one of the severe types. Only an experienced dermatologist can differentiate between the various types of eczema. The symptoms may appear similar to the general population.
Who Is Affected By Atopic Dermatitis?
The incidence of atopic dermatitis is the highest in the infant age affecting both males and females equally. As the child ages, the symptoms start to diminish. The skin in adults rarely presents itself with atopic dermatitis symptoms for the first time. Most cases that are treated by dermatologists are for infants, toddlers, and young children.
What Is The Treatment For Atopic Dermatitis?
When preventive measures fail to improve the skin’s condition and also when blisters (with or without any oozing fluid) are present, a medical intervention under the guidance of a dermatologist is necessary for atopic dermatitis (eczema) treatment . These are the treatments that are often prescribed depending on the severity of the diseases and the age of the affected person –
Also Read: How To Find The Best Dermatologist Near You
1. Topical Medications
Both corticosteroid and non-steroid creams and ointments are prescribed to alleviate the inflammation and the associated itchiness. Examples include tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. Crisaborole is another example of a topical medication used for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in babies and adults.
To help the skin in its repair process, topical creams such as Atopiclair and MimyX are prescribed to be used in conjunction with the steroid creams.
2. Oral Medications
Antibiotics are prescribed in the case of infected skin lesions to kill the microorganisms and to aid in the recovery of the skin cells. At times, even anti-histamines are recommended for oral consumption.
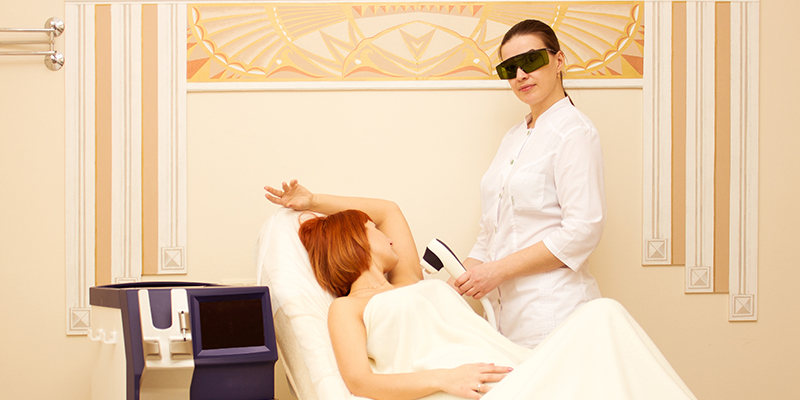
3. Phototherapy
This treatment uses ultraviolet A, B or both for atopic dermatitis in adults and children over 12 years of age. Mild to moderate level cases can be treated with phototherapy.
Apart from these treatment options, systemic corticosteroids (administered using injections) may be used in extreme cases, but this is very rare.
How To Prevent Atopic Dermatitis?
Many a times, atopic dermatitis in infants and adults can be managed by eliminating the triggers from the surroundings.
- Avoid irritants and allergens in clothing or food.
- Opt for short baths with cool water, instead of hot or warm water as it can make the skin dry.
- Use gentle cleansers for atopic dermatitis on the face.
- A non-allergic body wash or soap meant for use on sensitive skin should be used.
- Harsh detergents and soaps should be avoided at all times.
- Use a hydrating moisturizer (without any allergenic components) to keep the dryness at bay.
Treating and managing atopic dermatitis is vital, especially because it affects infants in most cases. Get the right advice and help that you need by consulting a dermatologist in order to understand this skin condition and its management better. Do not let it progress and cause unnecessary complications as a timely course of treatment and easy-to-follow preventive tips can go a long way.